Brief introduction of laser accelerator
Since the world's first accelerator was built, human beings have gradually deepened their understanding of the micro material world, and great achievements have been made in the research of basic physics. Accelerator uses a certain form of electromagnetic field to accelerate charged particles such as electrons, protons or heavy ions. It is an important tool for people to study the deep structure of matter.
Accelerator science usually involves many scientific and technological fields such as microwave, vacuum, precision machining and manufacturing, automatic control, high-performance computing, data transmission and processing, plasma and laser. With the continuous emergence of new technologies and principles in these fields, accelerator science has also achieved continuous development. On the one hand, its research and development have important applications in other disciplines such as biology, material science, solid physics, chemistry, geology, archaeology and so on; On the other hand, it is also widely used in the fields of nuclear fuel detection and tumor treatment.
It can be seen that the development level of accelerator technology is closely related to the national economy and the status and security of the country, and usually becomes an important symbol to measure the comprehensive national strength. Accelerator equipment is generally restricted by large scale, large investment and high operation cost. It usually only exists in a few large national laboratories. Due to the limitation of funds, space and site and the limited beam time, it is difficult to meet the needs of many applications such as tumor treatment and high brightness X-ray source (such as the fourth generation free electron laser).
The electric field gradient of the laser accelerator is three orders of magnitude higher than that of the conventional RF accelerator, which can reduce the size of the accelerator by a thousand times, turn the Application Accelerator into a "table size", no longer "expensive" and "huge", and can be settled in small and medium-sized laboratories and research institutes.
About CLAPA
The Compact Laser Plasma Accelerator Laboratory of Peking University put forward the new principle of laser steady-phase acceleration and the new method of critical density plasma lens for the first time in the world, carried out and confirmed the steady-phase acceleration experiment for the first time, broke the energy record of femtosecond laser driven carbon ions twice, and is expected to promote the application of the new accelerator. The laboratory will further devote itself to the research on acceleration and radiation in the process of laser plasma interaction, and explore the feasibility of generating TEV PEV high-energy particles in theory. At the same time, it will build a new ultra small mesa laser particle accelerator and carry out application research such as cancer treatment, plasma diagnosis and ion fast fire fusion in the next few years.
The Compact Laser Plasma Accelerator (CLAPA) Laboratory of Peking University is subordinate to the Institute of Heavy Ion Physics, School of physics, Peking University. The laboratory officially carried out research on laser plasma acceleration in 2005. Combined with the basic background of traditional accelerator, the team quickly made a breakthrough in theory. Professor Yan Xueqing's team found that in the case of circular polarization, when the laser focusing light intensity and solid surface density meet certain conditions, the electrostatic field formed under the action of laser mass dynamics can not only accelerate protons, but also focus the beam longitudinally: that is, the steady-phase light pressure acceleration mechanism.
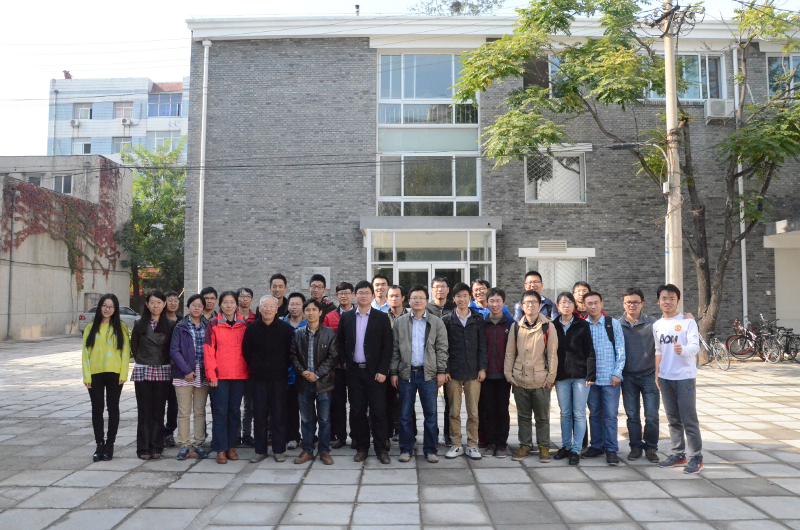

From 2012 to 2017, supported by the major instrument project of the Ministry of Science and Technology, the laser acceleration team of Peking University has overcome key technologies such as high contrast and high light intensity laser technology, self-supporting nano film target preparation technology, ultra-high current intensity ion beam transmission technology and laser accelerator irradiation research platform, and finally built the world's first small laser accelerator irradiation device.
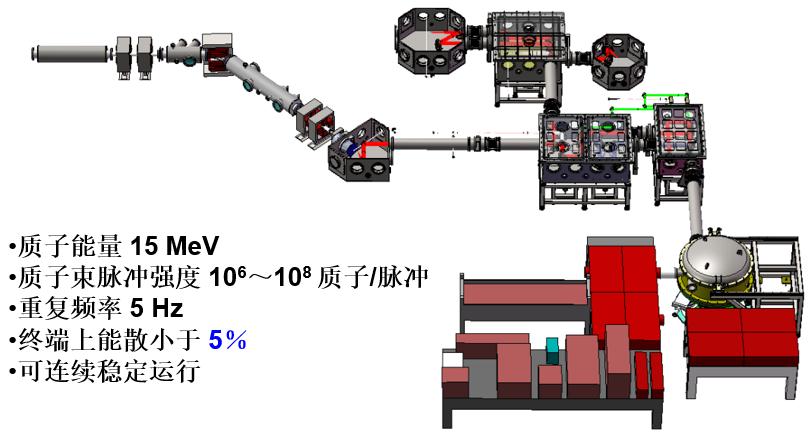
The CLAPA laser accelerator system has been built in Peking University
In 2019, the Ministry of Science and Technology further supported the laboratory's research and application demonstration of petawatt laser proton accelerator device. This project gives full play to the advantages of Peking University and its partners in scientific research and talent training, and creates a rigorous and harmonious academic environment. Based on the disciplines of many advantageous disciplines of Peking University and other institutions and units, the project further integrated engineering and technical experts with rich experience in instrument R & D, cultivated a group of high-quality, high-level and interdisciplinary comprehensive research talents, established a high-level laser Accelerator Research and application team, and jointly tackle key problems of major scientific instruments.
The main talents of the project include 4 academicians (Chen Jiaer, he Xiantu, Du Xiangwan and Zhang Weiyan), 1 outstanding youth (Yan Xueqing), 4 selectees of Thousand Talents program (MA Wenjun, Fu engang, Li Bo and Qiao bin), chief physician of Beijing Cancer Hospital (Wu Hao), and 5 engineers. It provides a guarantee for the smooth completion of the project. The leading unit and the project patners have more than 20 fixed personnel engaged in laser accelerator and application, and more than 40 graduate and doctoral students. The project will land in the "Beijing laser accelerated innovation center" of Huairou Science City, Beijing.
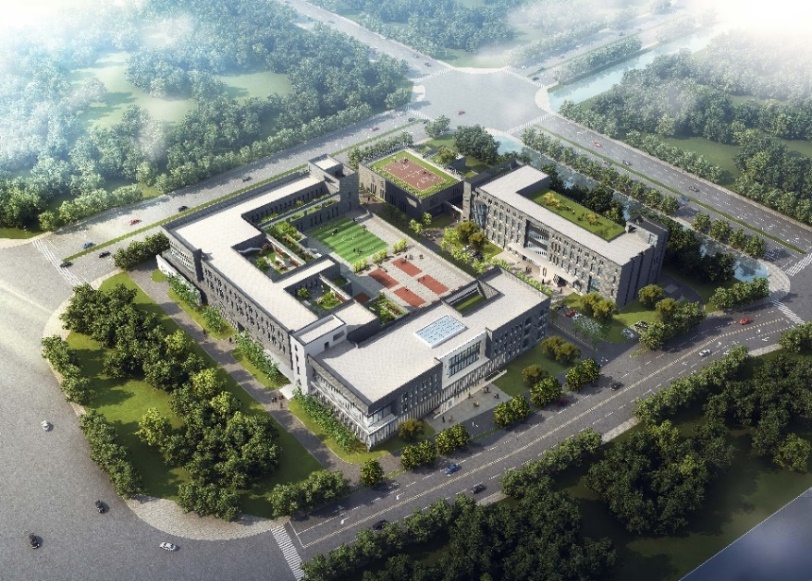

Beijing Laser Center for accelerating innovation
Beijing Laser Acceleration Innovation Research Center is located in HR00-0011-6040 Basic Research Aggregation Area of Huairou Science City (Block 11, Huairou New City), north to Beijing Light Element Quantum Material Crossing Platform, west to Huairou Qingnian Road, south to 100 meters north of Huairou Yongle Street, east to Yanqi Seventh Road, it shares the same plot with Beijing Light Element Quantum Materials Cross-Platform Project, with a total construction area of 30,000 square meters, it mainly includes a laser proton acceleration application research platform and a process support platform. After completion, the infrastructure can support the research and development of future laser proton radiotherapy system, laser-driven gamma light source, gamma light source, and laser-driven broad-spectrum coherent light source. A total of 300 R&D and related staff are required.